Table of Contents
- Normal pediatric ultrasound measurements
- Liver/RUQ ultrasound normals
- TIPS evaluation
- Liver transplant evaluation
- Retroperitoneal US normals
- Renal transplant evaluation
- Fetal/pediatric hydronephrosis
- Female reproductive normals
- Adnexal cyst follow up guidelines
- First trimester ultrasound/pregnancy of unknown location
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Carotid ultrasound
Normal Pediatric Ultrasound Measurements
LIVER/RUQ
Sources:
Normals
| Gallbladder Wall | <3mm |
| CBD | <6mm, add 1mm per decade >70 years |
| MPV | <13mm |
| IVC | 12-17mm |
| Hepatic Artery RI | 0.55-0.7 |
TIPS Evaluation
| Direct Signs of TIPS malfunction | Indirect signs |
| Shunt velocity <90cm/s OR >/= 190cm/s Increase or decrease in velocity by >50cm/s | MPV velocity >30cm/s Collateral vessels (new, increased) Ascites (new, increased) R-L portal venous flow reversal (hepatopetal) |

Variations in TIPS placements 
Liver transplant evaluation
Complications
- IVC stenosis/thrombosis
- Biliary strictures, stones or sludge, dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, and recurrent disease
- Most within 3-6 months of transplant
- Parenchymal infarcts and abscesses 2/2 hepatic artery complications
- Fluid collections and ascites
Normal findings
| RI | 0.5-0.7 |
| Hepatic artery | Rapid systolic upstroke with continuous diastolic flow |
| Hepatic vein | Phasic flow pattern |
| Portal vein | Continuous hepatopetal flow |
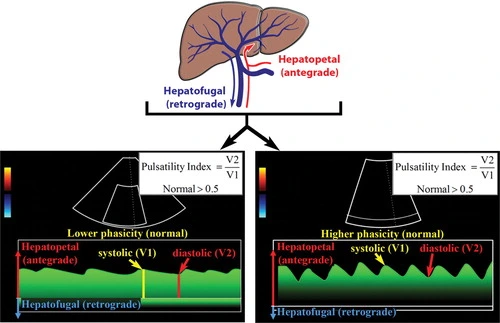
Normal MPV waveforms 
Normal hepatic vein and artery waveforms
RETROPERITONEAL ULTRASOUND
| Renal cortex | Less echogenic than liver >6mm thickness |
| Medullary pyramids | Less echogenic than cortex |
| Renal sinus | More echogenic than cortex |
| Parenchymal thickness | 15-20mm |
| Renal size | 10-14 cm long in males 9-13 cm long in females |
Renal Transplant
Complications
| Renal artery RI | Normal 0.5-07 >0.7 indicated graft dysfunction |
| Parenchymal edema | Graft dysfunction (nonspecific) |
| Renal vein thrombosis/stenosis | Reversal of diastolic flow |
| Renal artery thrombosis/stenosis | PSV >200cm/s >2:1 velocity ∆ between segments Post-stenotic spectral widening Parvus et tardus waveform distal to stenosis |
| Pseudoanuerysm | Ying/yang sign |
| AVF | High-velocity, low resistance flow within the artery May see vibration “mosaic” color on Doppler |
Graft dysfunction
- ATN/Rejection
- Nephrotoxicity (drugs)
- Recurrent disease
- Pyelonephritis
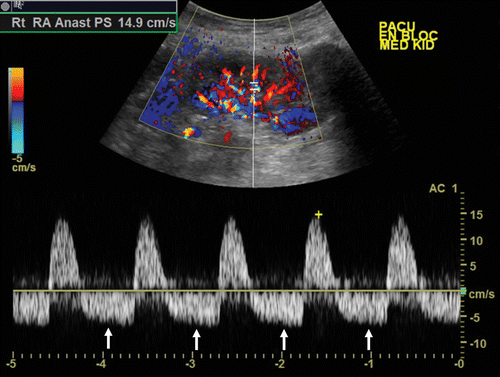
Reversal of diastolic flow in renal vein thrombosis 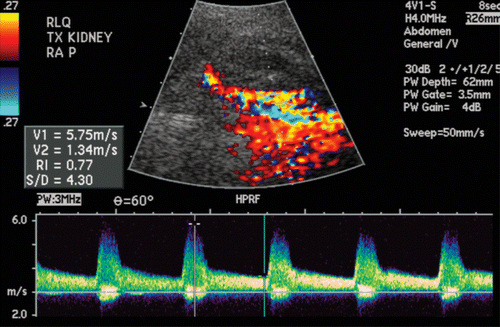
Elevated PSV in renal artery stenosis 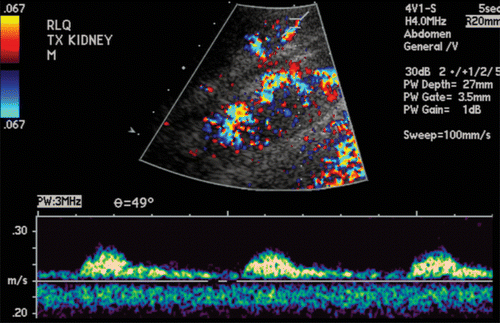
Upstream parvus et tardus waveform in renal artery stenosis
Perinephric fluid collections
| Collection | Timeline | Imaging |
| Hematoma | 0-5 days | Complex heterogenous collection Internal septations/retracting clot |
| Abscess | wks-mo | Increased peripheral blood flow on Doppler Thick wall |
| Urinoma | 0-10 days | Simple collection with anechoic fluid |
| Lymphocele | 2wk-6mo | Fluid collection ± thin internal septa, usually adjacent to kidney |
Timeline of post-transplant complications
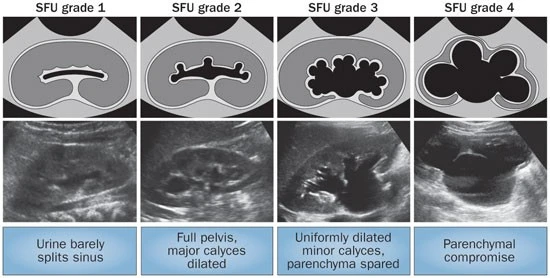
Grading Fetal/Pediatric Hydronephrosis
Female Reproductive
| Pre-menopausal endometrial thickness | 3-15mm |
| Post-menopausal endometrial thickness | No bleeding: <8mm Bleeding: <5mm |
| Pre-menopausal ovarian volume | 4-16mL |
| Post-menopausal ovarian volume | 1.2-5.8mL |
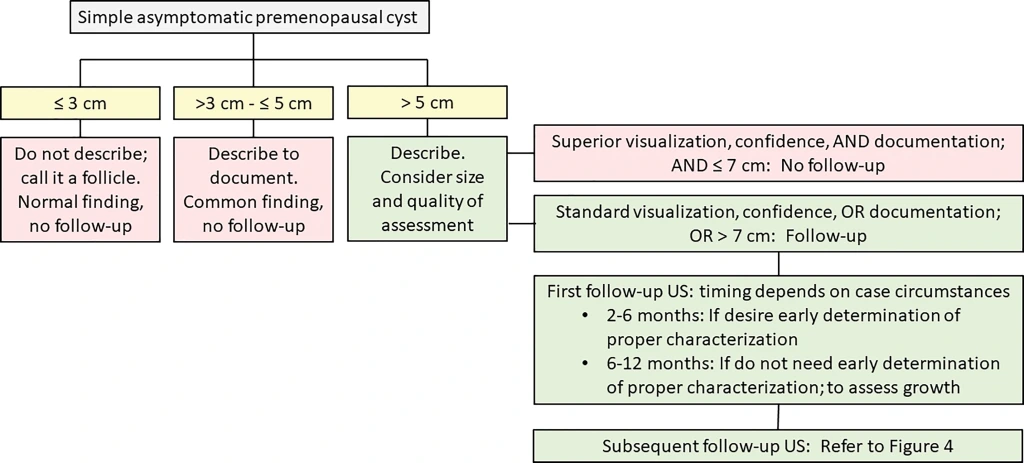
Adnexal Cysts
Pre-menonpausal Female
Post-menopausal Females

Follow-up Exam Guidelines

First Trimester Ultrasound
Sources
General Principles

- Discriminatory zone of beta-hcg: >2,000-3,000
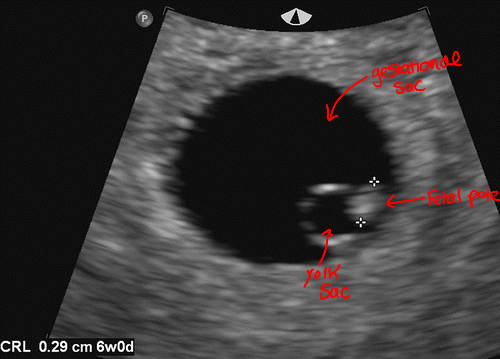
- Should see yolk sac by 5.5 weeks
- Should see fetal pole by 6 weeks
- Should see yolk sac once gestational sac is 8mm
- Should see fetal pole once gestational sac is 16mm
- Fetal demise if gestational sac 25mm and no fetal pole
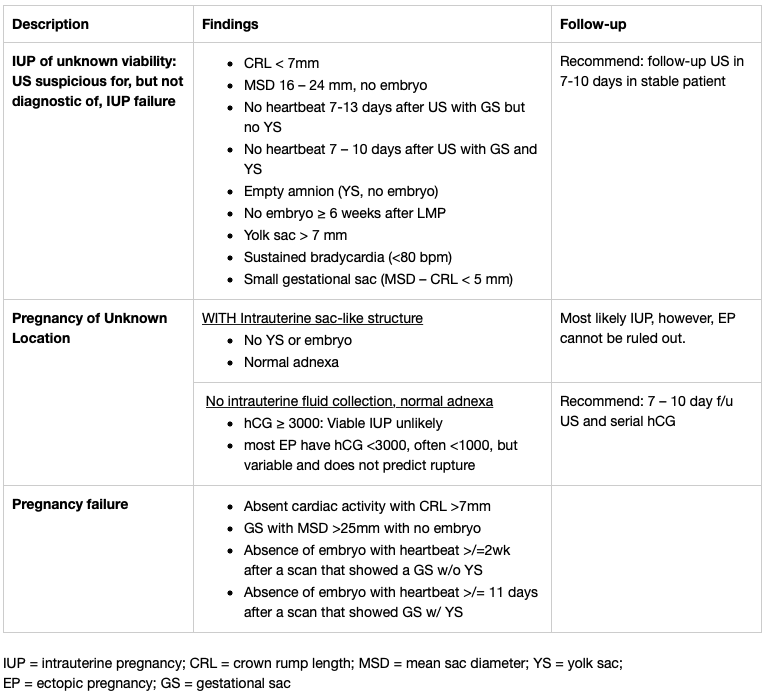
SRU Criteria
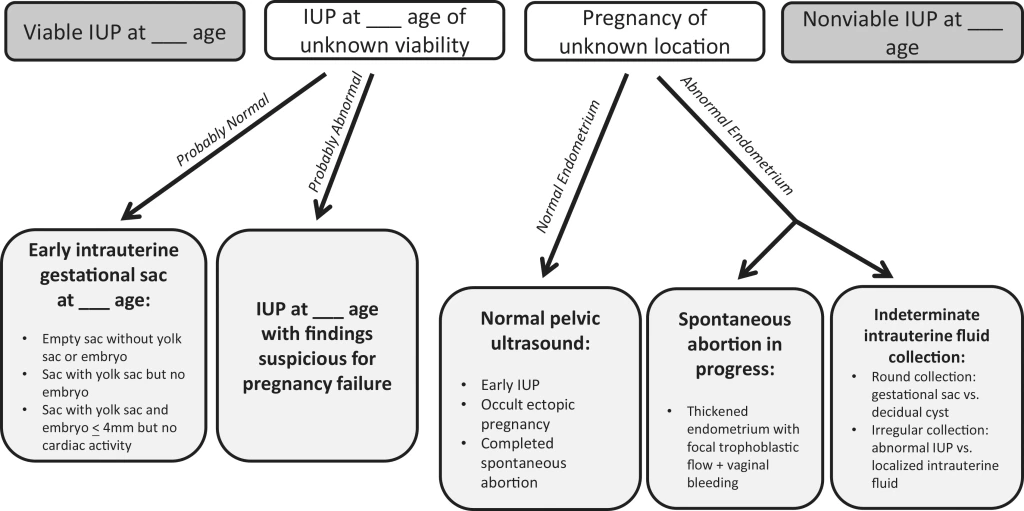

Pregnancy of Unknown Location
Expectant management should only be recommended in asymptomatic patients
Increasing pain, hemorrhage, increasing or stable hCG DO NOT RECOMMEND EXPECTANT MANAGEMENT
Serial hCG q48hrs and TVUS required
- Nonviable IUP most likely when hCG >2000 mIU/mL
- hCG 2000-3000 mIU/mL
- Likelihood of viable IUP is around 2%
- Nonviable IUP 38x as likely as viable IUP and 2x as likely as ectopic pregnancy
- Follow up with US and repeat hCG testing
- hCG >3000 mIU/mL
- Viable IUP is possible but unlikely <0.5%
- Nonviable IUP is most likely
- At least one F/u hCG and TVUS
- Ectopic 70x more likely than viable IUP
- hCG 2000-3000 mIU/mL
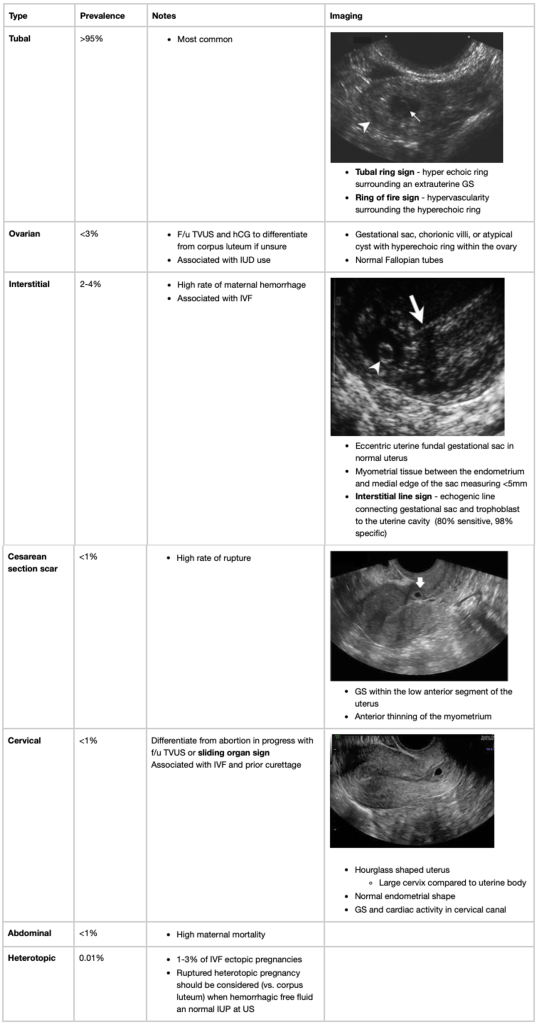
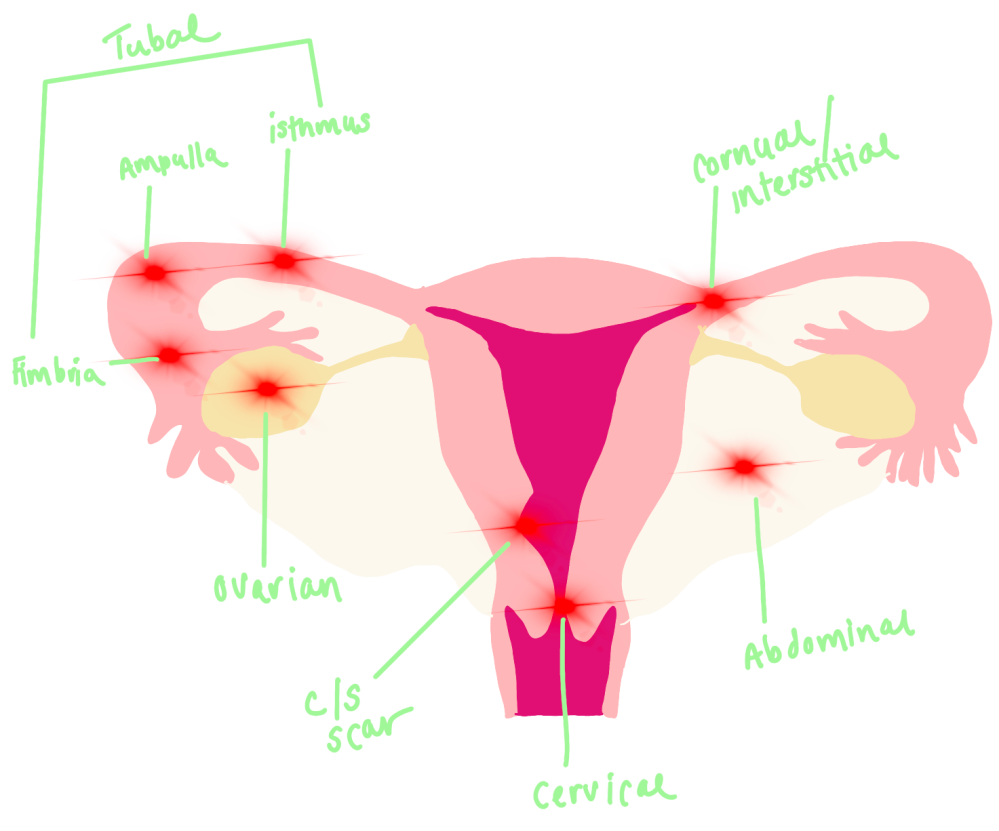
Ectopic Pregnancy
General Principles
- Patients with ectopic have slower hCG rise than women with normal IUP
- <53% hCG increase over 48 hours, pregnancy almost always nonviable (99% sensitivity)
- Sensitivity and specificity of transvaginal ultrasound findings
- Extrauterine live embryo with cardiac activity – 100% specific
- Adnexal mass separate from ovary
- Yolk sac (YS) and embryo – most specific
- Tubal ring with YS only OR no central identifying features – less specific
- Complex extra ovarian adnexal mass
- Ring of fire sign
- Not specific – more common with corpus luteum
- Complex pelvic free fluid – rupture
- 86-93% PPV with abnormal hCG
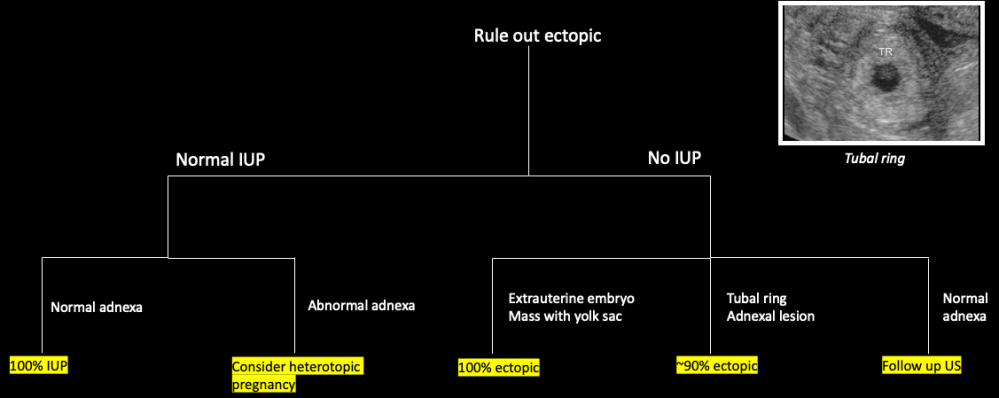
Intrauterine Findings in Ectopic Pregnancy
- SRU 2013
- For pregnancy of unknown location, intrauterine round or oval fluid collection is much more likely to be an IUP than a pseudo gestational sac or decidual cyst
- Pseudogestational sac
- 10-20% of ectopic pregnancies
- Surrounding thick decidual reaction and absent arterial flow
- Angular or teardrop appearance
- Central location distinguishes from decidual cysts and intradecidual sac

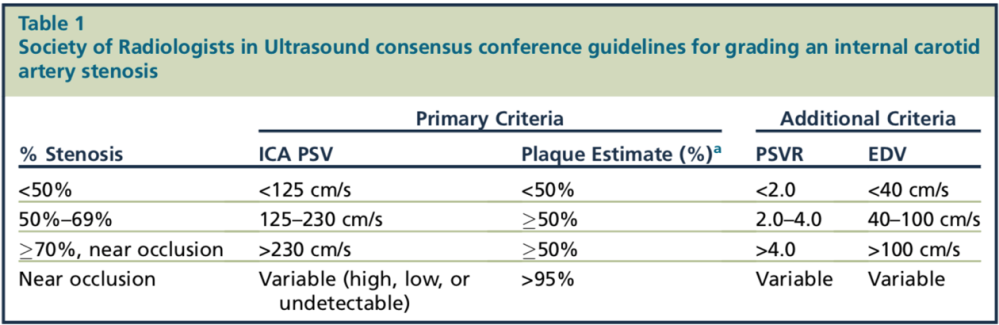
Carotid Ultrasound
Look at the plaque, degree of stenosis, and carotid waveforms