Table of Contents
- Fleischner Criteria
- Basic differential for lung parenchymal findings
- Expanded differential for ground glass opacities
- Pulmonary CT signs differential
- Thoracic lymph node stations
- Pulmonary arterial anatomy
- PE classification
- Normal aortic measurements
- Acute aortic syndrome
- Aortic dissection classification
- Traumatic aortic injury
- Endoleaks
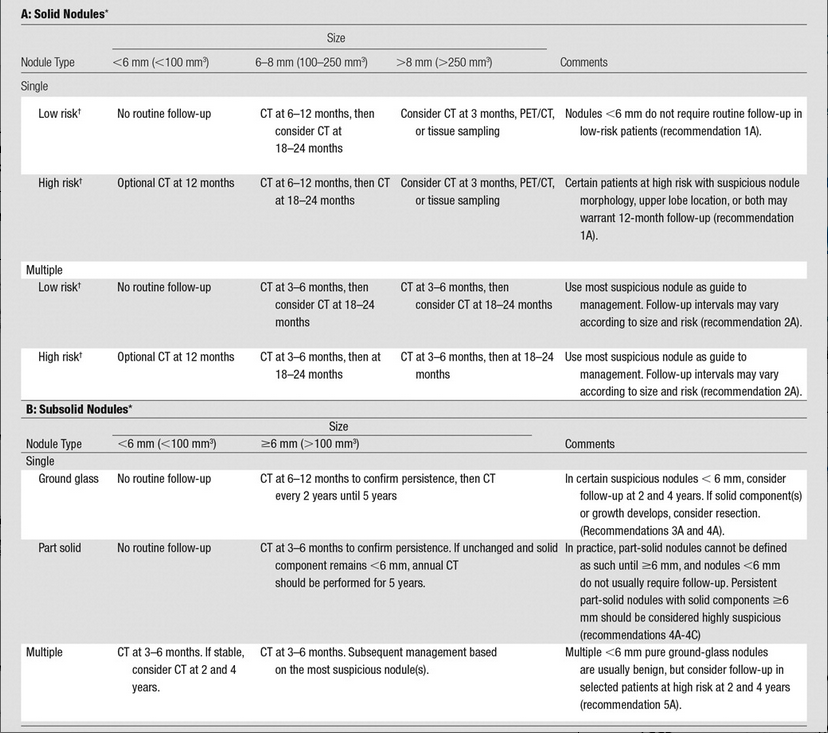
Fleischner Criteria (2017)
Basic Differential for Lung Parenchymal Findings

Expanded Differential for Ground Glass Opacities

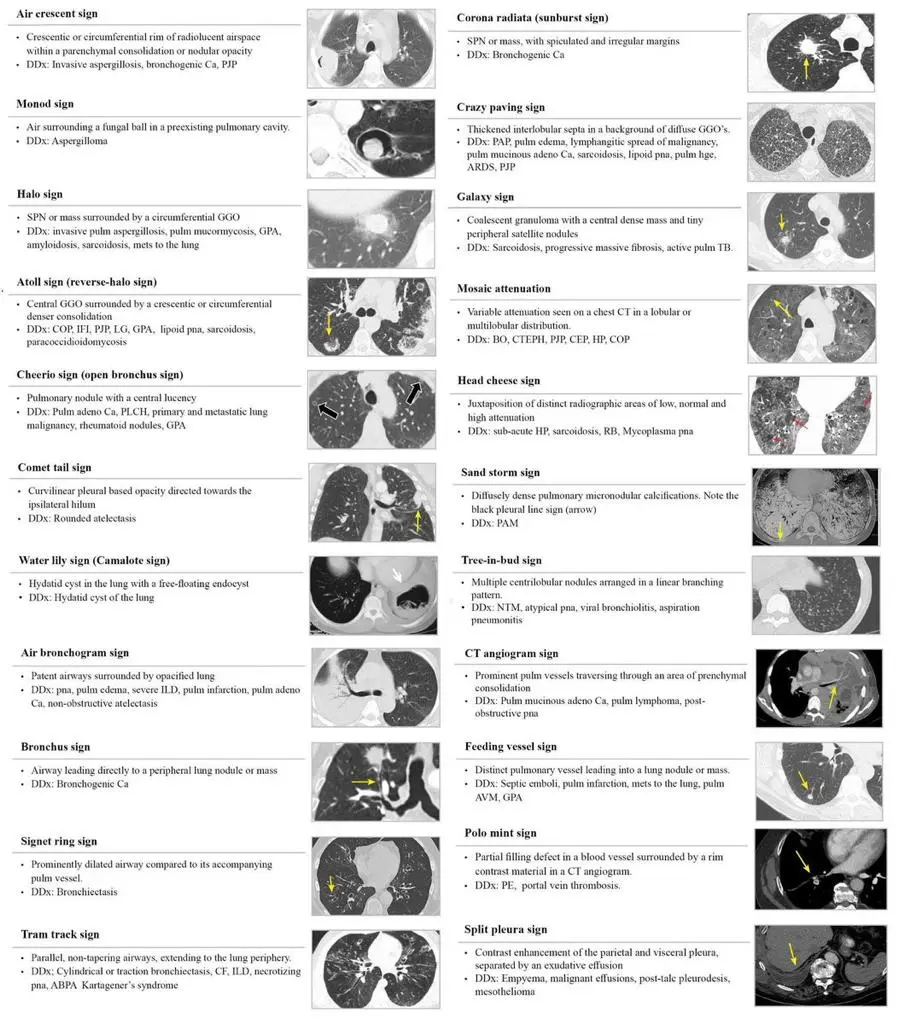
Pulmonary CT Signs and Differential
Lymph Node Stations
Annotated CT
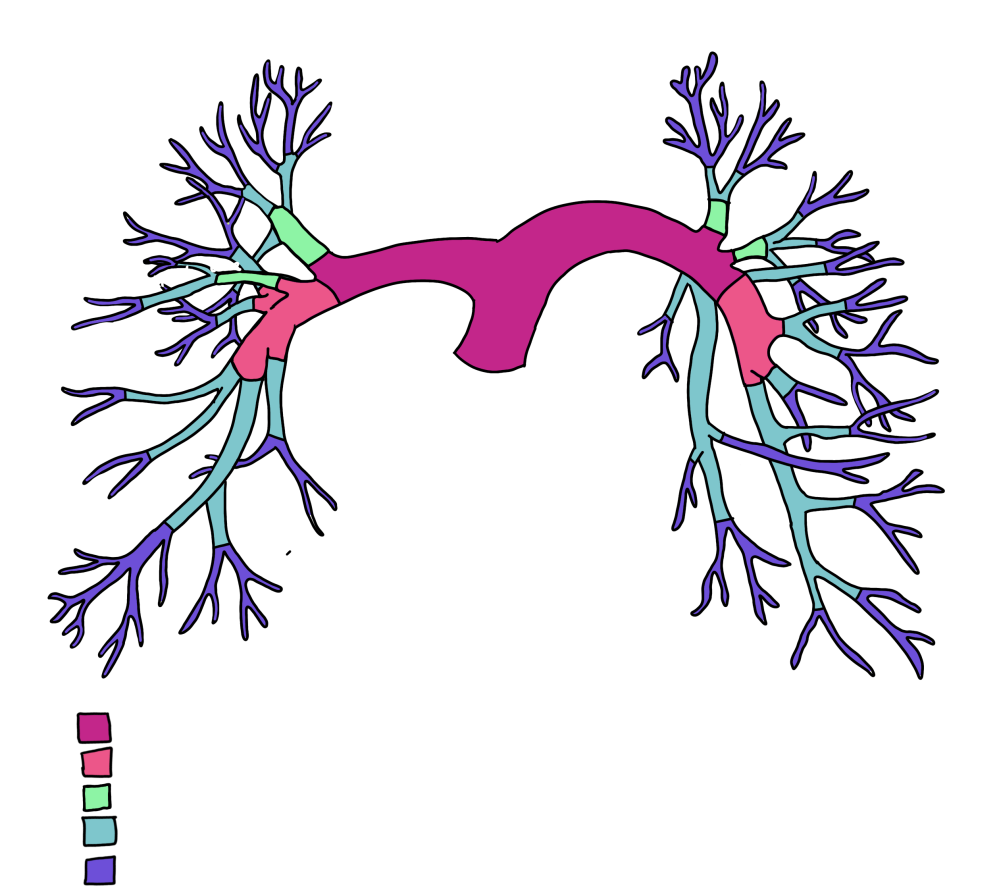
General Pulmonary Arterial Anatomy
PE Classification
| Category | Criteria | Mortality Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Massive | Acute PE with sustained hypotension (< 90mmHg systolic) for >15 minutes OR requiring inotropic support | 25-65% |
| Submassive | Systolic >90mmHg with either findings of right heart strain (CT, ECG, BNP) or elevated troponins | 3% |
| Low risk | None of the above | <1% |
Normal Aortic Measurements

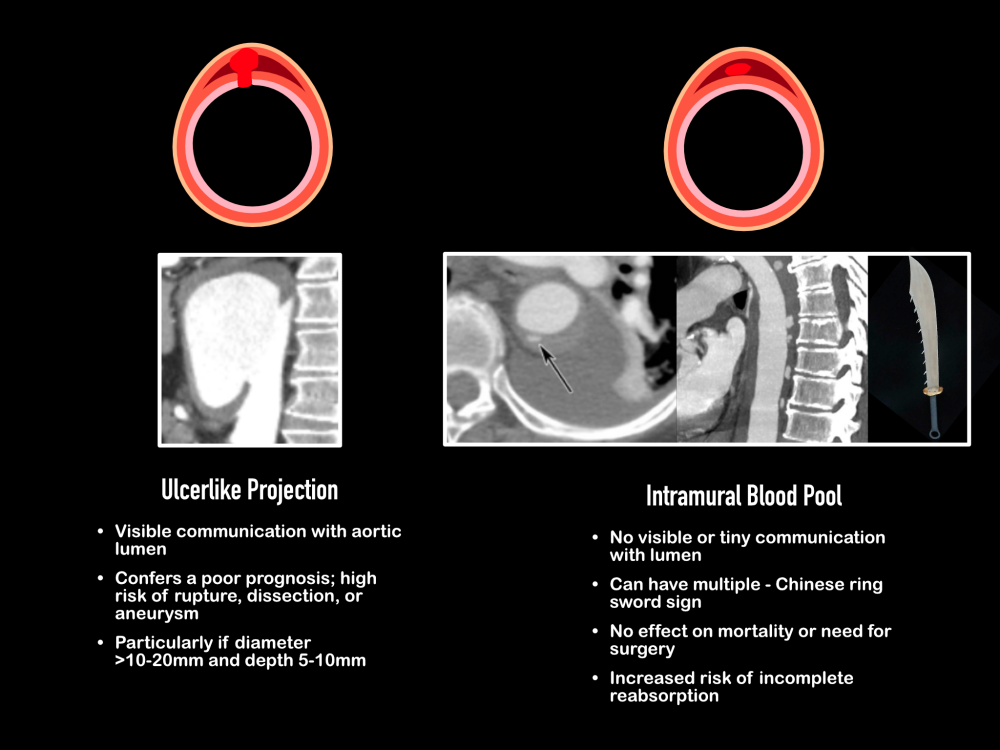
Acute Aortic Syndrome
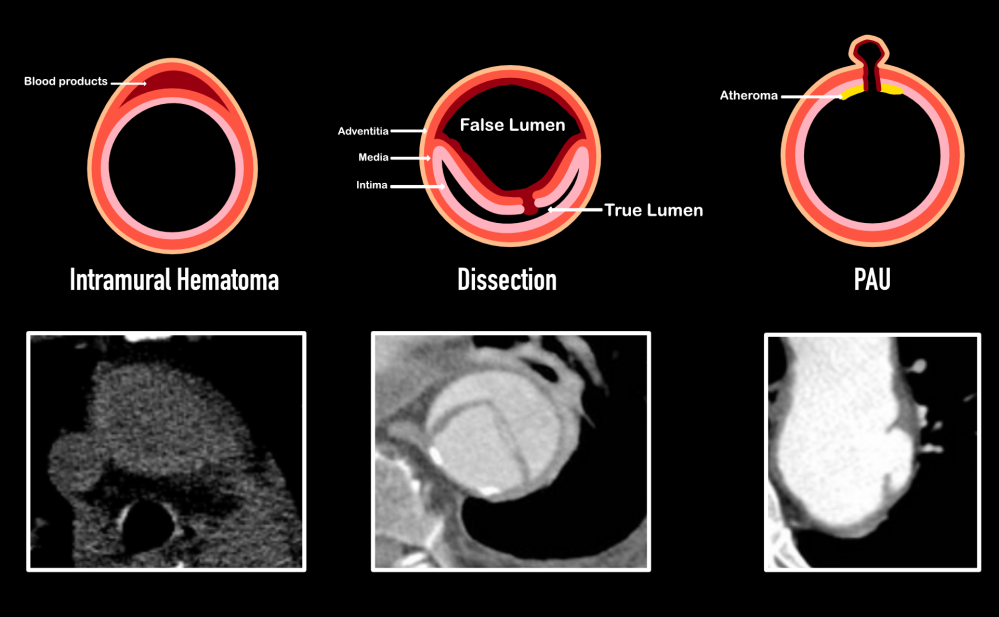
Intramural Hematoma
Reporting Checklist
- Stanford Classification
- Maximum aortic diameter (generally >5cm = surgery)
- Maximal hematoma thickness (generally >11mm = surgery)
- Presence of intramural blood pool or ulcer like projections
- Ulcer like projection diameter and depth
- Presence of
- Pleural effusion
- Pericardial effusion
- Periaortic hematoma
Aortic Dissection

Reporting Checklist
- Diagnosis
- Standard dissection
- Incomplete dissection
- Distribution
- Entry and exit tear sites
- Branch vessel origins from the true/false lumen
- If type B and endograft may be attempted:
- Size of the vertebral arteries
- Distance from the left subclavian to the entry tear
- Distance from the left common carotid to the left subclavian
- Complications
- Rupture
- Shared sheath rupture
- Hemopericardium
- Aortic insufficiency
- Intimointimal intussusception
- Coronary involvement
- Signs of organ ischemia
- Rupture
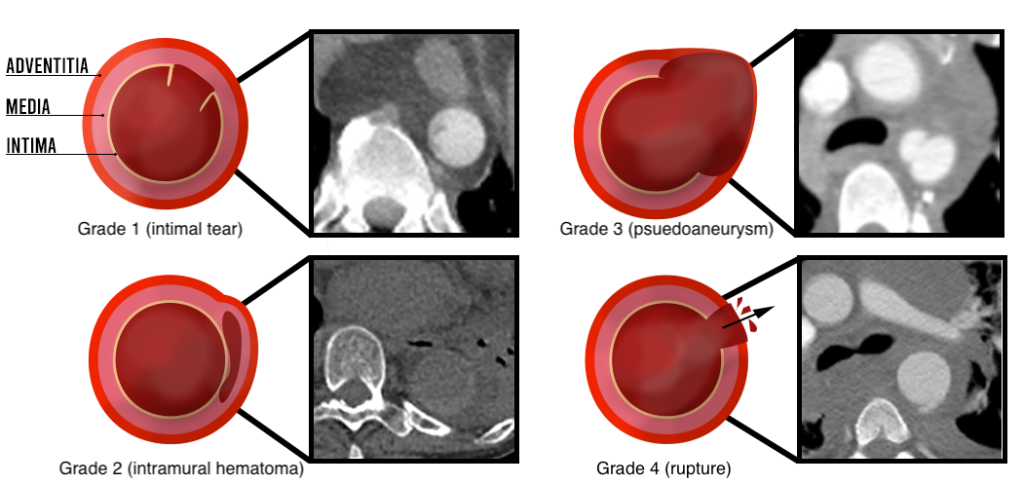
Traumatic Aortic Injury
Endoleaks
